P O I N T S :
- a point is a geometric entity which has no dimentions in space .
- a sequence of dots is called a line .
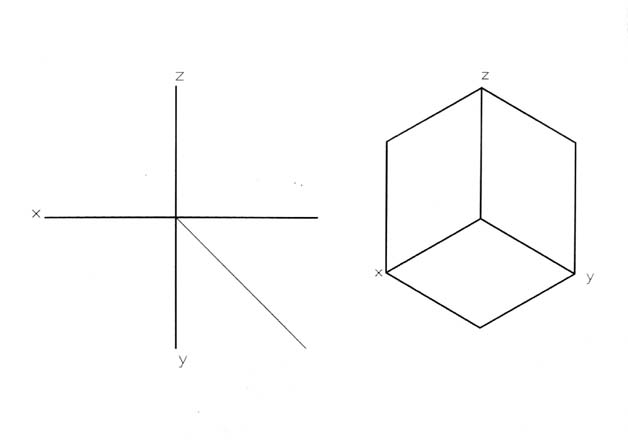
- the lines created at the junction of the three planes - are called A X E S , and are
marked by the letters : X , Y , Z .
- it is possible to locate and describe each point in space on picture-planes - by projecting rays through the point - to the picture-planes ,
and which are perpendicular them .
- the location of a point in space is marked by its distance from the center of axes - and is represented by three letters (each standing for a numerical value) -
inside parenthasis .
- the point is usually represented by a latin letter , and its location in space is described like this : P ( a , b , c ) .
the letter a = stands for the distance
of the point along the X axes .
the letter b = stands for the distance
of the point along the Y axes .
the letter c = stands for the distance
of the point along the Z axes .
- the point which is located at the junction point of the three planes - is marked ( 0 , 0 , 0 ) , because its distance from each of the three
planes , is - zero .
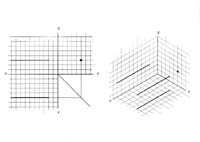
the plane on which the top-view is projected is called = π1
the plane on which the front-view is projected is called = π2
the plane on which the side-view is projected is called = π3
- each point has two numerical values on each plane :
- on π1 we have the distances of a point from the Y axis , and from the X axis .
- on π2 we have the distances of a point from the Z axis , and from the X axis .
- on π3 we have the distances of a point from the Z axis , and from the Y axis .
The importance of knowing how to locate - a POINT , a LINE , and a PLANE :
- The art of describing three dimentional objects on our paper is a most important and basic skill in all drafting languages :
- The first step is to locate one point on our paper , then another ( the thechnique of describing all points in space on our paper - is identical ) and as many as we
need .
Once we have the points - we can connect one to another , and create lines .
and once we have lines , we conect lines to each other to create planes , and by connecting
planes - we are able to get complete views of three dimentional objects - on our two dimentional paper .
each pair of projection picture-planes is called - ADJACENT PLANES :
- every two views of the same point on adjacent planes - are connected between themselves by an auxiliary line which is called - d u o l i n e .
- a
DUO - LINE is a straight line which is perpendicular to the axis located between two adjacent planes .
- the distances of a point from the two adjacent planes are measured on the duo line .
- when the two adjacent planes are π1 and
π2 the distance from π2 appears on
π1 and the distance of the point from π1
appears on π1 .
different P O I N T S :
- a P L A N A R P O I N T is a point whose
coordinate distance from any one of the planes is zero .
- an A X I A L P O I N T is a point which two
of its coordinate distances from the planes are zero .
- a C E N T E R P O I N T is a point whose all
three coordinate distances from the planes are zero .
- a T H R E E D I M E N T I O N A L P O I N T is a point whose all
three coordinate distances are not zero .
H I D D E N P O I N T S :
- a L I N E is made up of an infinite number of points .
- a L I N E S E G M E N T is a part of a line which is bounded by a point at
its beginning and by a point at its end .
- a point of a line which is hidden to us by a point in front of it , is called a h i d d e n p o i n t .
such a situation occures when we can see the only the first point of the segment of a straight line because the rest of the segment is lined away from us
perpendicular to our horizon line ( the height of our eyes ) .
In this case - the whole line is hidden behind its first point - and we see a whole line as one point only.
projections of a hidden point
M O R E V I E W S of a P O I N T :
- there are situations when we want to show the line which is hidden behind its first point .
in such a case we must add more projection planes , besides the one we already have ( which shows the whole line as one point ) ,
and then we can see other views of the line , - on the added planes , from different positions .

